更新時間:2019-09-11 11:54:07 來源:動力節點 瀏覽2301次
動力節點java培訓機構小編分享的“JAVA中異常與異常處理詳解”的內容太長,請看上文:http://m.dabaquan.cn/javazixun/1828.html
Java自定義異常
如果要自定義異常類,則擴展Exception類即可,因此這樣的自定義異常都屬于檢查異常(checked exception)。如果要自定義非檢查異常,則擴展自RuntimeException。
按照國際慣例,自定義的異常應該總是包含如下的構造函數:
一個無參構造函數
一個帶有String參數的構造函數,并傳遞給父類的構造函數。
一個帶有String參數和Throwable參數,并都傳遞給父類構造函數
一個帶有Throwable 參數的構造函數,并傳遞給父類的構造函數。
下面是IOException類的完整源代碼:
public class IOException extends Exception
{
static final long serialVersionUID = 7818375828146090155L;
public IOException()
{
super();
}
public IOException(String message)
{
super(message);
}
public IOException(String message, Throwable cause)
{
super(message, cause);
}
public IOException(Throwable cause)
{
super(cause);
}
}
Java異常的注意事項
1、當子類重寫父類的帶有 throws聲明的函數時,其throws聲明的異常必須在父類異常的可控范圍內——用于處理父類的throws方法的異常處理器,必須也適用于子類的這個帶throws方法 。這是為了支持多態。
例如,父類方法throws 的是2個異常,子類就不能throws 3個及以上的異常。父類throws IOException,子類就必須throws IOException或者IOException的子類。
示例:
class Father
{
public void start() throws IOException
{
throw new IOException();
}
}
class Son extends Father
{
public void start() throws Exception
{
throw new SQLException();
}
}
/**********************假設上面的代碼是允許的(實質是錯誤的)***********************/
class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Father[] objs = new Father[2];
objs[0] = new Father();
objs[1] = new Son();
for(Father obj:objs)
{
//因為Son類拋出的實質是SQLException,而IOException無法處理它。
//那么這里的try。。catch就不能處理Son中的異常。
//多態就不能實現了。
try {
obj.start();
}catch(IOException)
{
//處理IOException
}
}
}
}
2、Java程序可以是多線程的。每一個線程都是一個獨立的執行流,獨立的函數調用棧。如果程序只有一個線程,那么沒有被任何代碼處理的異常 會導致程序終止。如果是多線程的,那么沒有被任何代碼處理的異常僅僅會導致異常所在的線程結束。
也就是說,Java中的異常是線程獨立的,線程的問題應該由線程自己來解決,而不要委托到外部,也不會直接影響到其它線程的執行。
finally塊和return
首先一個不容易理解的事實:在 try塊中即便有return,break,continue等改變執行流的語句,finally也會執行。
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int re = bar();
System.out.println(re);
}
private static int bar()
{
try{
return 5;
} finally{
System.out.println("finally");
}
}
/*輸出:
finally
*/
很多人面對這個問題時,總是在歸納執行的順序和規律,小編總結了一個方法。用如下GIF圖說明。
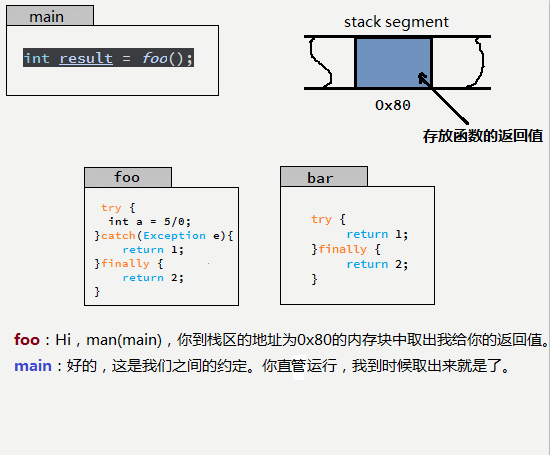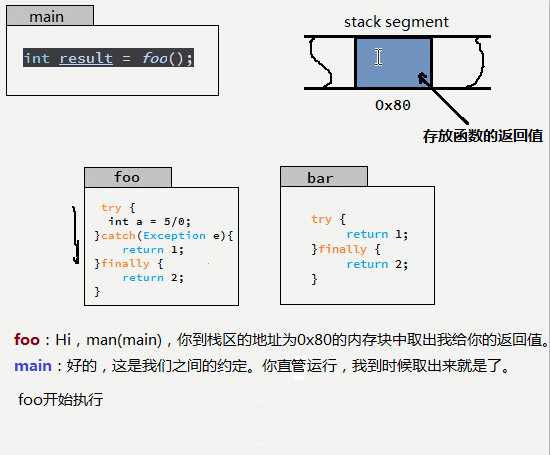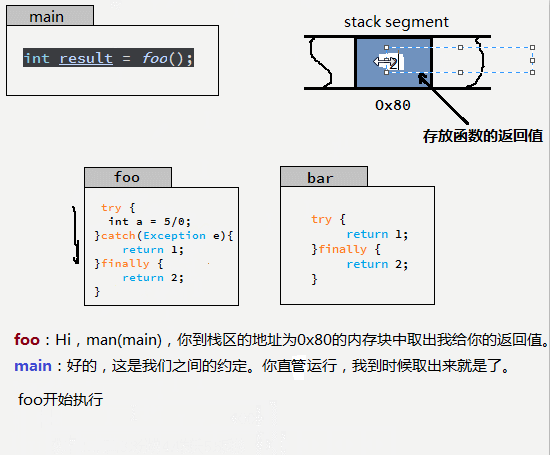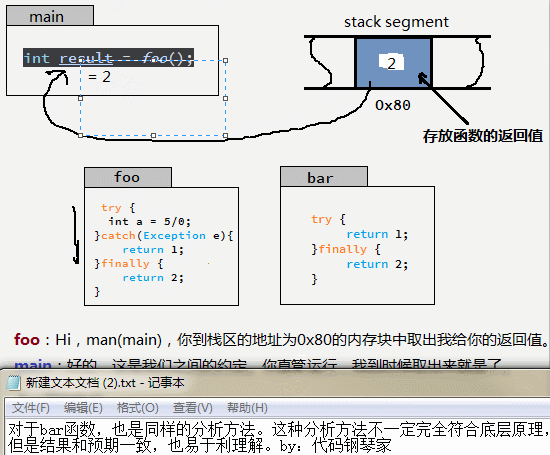
也就是說:try...catch...finally中的return 只要能執行,就都執行了,他們共同向同一個內存地址(假設地址是0x80)寫入返回值,后執行的將覆蓋先執行的數據,而真正被調用者取的返回值就是最后一次寫入的。那么,按照這個思想,下面的這個例子也就不難理解了。
finally中的return 會覆蓋 try 或者catch中的返回值。
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int result;
result = foo();
System.out.println(result); /////////2
result = bar();
System.out.println(result); /////////2
}
@SuppressWarnings("finally")
public static int foo()
{
trz{
int a = 5 / 0;
} catch (Exception e){
return 1;
} finally{
return 2;
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("finally")
public static int bar()
{
try {
return 1;
}finally {
return 2;
}
}
finally中的return會抑制(消滅)前面try或者catch塊中的異常
class TestException
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int result;
try{
result = foo();
System.out.println(result); //輸出100
} catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage()); //沒有捕獲到異常
}
try{
result = bar();
System.out.println(result); //輸出100
} catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage()); //沒有捕獲到異常
}
}
//catch中的異常被抑制
@SuppressWarnings("finally")
public static int foo() throws Exception
{
try {
int a = 5/0;
return 1;
}catch(ArithmeticException amExp) {
throw new Exception("我將被忽略,因為下面的finally中使用了return");
}finally {
return 100;
}
}
//try中的異常被抑制
@SuppressWarnings("finally")
public static int bar() throws Exception
{
try {
int a = 5/0;
return 1;
}finally {
return 100;
}
}
}
finally中的異常會覆蓋(消滅)前面try或者catch中的異常
class TestException
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int result;
try{
result = foo();
} catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage()); //輸出:我是finaly中的Exception
}
try{
result = bar();
} catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage()); //輸出:我是finaly中的Exception
}
}
//catch中的異常被抑制
@SuppressWarnings("finally")
public static int foo() throws Exception
{
try {
int a = 5/0;
return 1;
}catch(ArithmeticException amExp) {
throw new Exception("我將被忽略,因為下面的finally中拋出了新的異常");
}finally {
throw new Exception("我是finaly中的Exception");
}
}
//try中的異常被抑制
@SuppressWarnings("finally")
public static int bar() throws Exception
{
try {
int a = 5/0;
return 1;
}finally {
throw new Exception("我是finaly中的Exception");
}
}
}
注意:
不要在fianlly中使用return。
不要在finally中拋出異常。
減輕finally的任務,不要在finally中做一些其它的事情,finally塊僅僅用來釋放資源是最合適的。
將盡量將所有的return寫在函數的最后面,而不是try ... catch ... finally中。
以上就是動力節點Java培訓機構小編介紹的“JAVA中異常與異常處理詳解”的內容,希望對大家有幫助,更多Java最新資訊請繼續關注動力節點Java培訓機構官網,每天會有精彩內容分享與你。
相關視頻教程推薦
java初級入門教程下載——Java自定義異常:http://m.dabaquan.cn/xiazai/1023.html
java初級入門教程下載——異常捕獲預處理:http://m.dabaquan.cn/xiazai/2555.html
 Java實驗班
Java實驗班
0基礎 0學費 15天面授
 Java就業班
Java就業班
有基礎 直達就業
 Java夜校直播班
Java夜校直播班
業余時間 高薪轉行
 Java在職加薪班
Java在職加薪班
工作1~3年,加薪神器
 Java架構師班
Java架構師班
工作3~5年,晉升架構
提交申請后,顧問老師會電話與您溝通安排學習

