更新時間:2022-08-04 10:44:41 來源:動力節(jié)點(diǎn) 瀏覽2173次
Java拷貝文件方法有哪些?動力節(jié)點(diǎn)小編來為大家總結(jié)了一下。使用java語言復(fù)制文件主要有3種方式。它們?nèi)缦滤荆?/p>
使用文件流(樸素方法)
使用 FileChannel 類
使用文件類。
注意:還有許多其他方法,例如 Apache Commons IO FileUtils,但我們僅討論使用 java 類復(fù)制文件。
這是一種天真的方法,我們使用文件輸入流從第一個文件中獲取輸入字符,并使用文件輸出流將輸出字符寫入另一個文件。這就像看到一個文件并寫入另一個文件一樣。
例子:
// Java Program to Copy file using File Stream
// Importing input output classes
import java.io.*;
// Main Class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
throws IOException
{
// Creating two stream
// one input and other output
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
// Initializing both the streams with
// respective file directory on local machine
// Custom directory path on local machine
fis = new FileInputStream(
"C:\\Users\\Dipak\\Desktop\\input.txt");
// Custom directory path on local machine
fos = new FileOutputStream(
"C:\\Users\\Dipak\\Desktop\\output.txt");
int c;
// Condition check
// Reading the input file till there is input
// present
while ((c = fis.read()) != -1) {
// Writing to output file of the specified
// directory
fos.write(c);
}
// By now writing to the file has ended, so
// Display message on the console
System.out.println(
"copied the file successfully");
}
// Optional finally keyword but is good practice to
// empty the occupied space is recommended whenever
// closing files,connections,streams
finally {
// Closing the streams
if (fis != null) {
// Closing the fileInputStream
fis.close();
}
if (fos != null) {
// Closing the fileOutputStream
fos.close();
}
}
}
}
輸出:
成功復(fù)制文件
對于上述程序,我們需要一個 input.txt 和一個 output.txt 文件。最初,兩個文本文件看起來像這樣
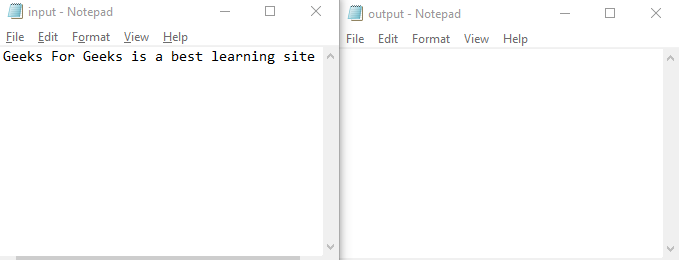
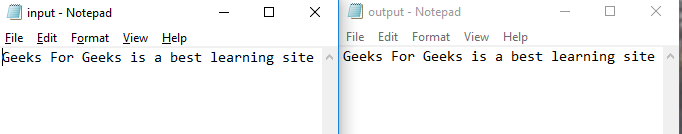
程序執(zhí)行成功后,
這是一個存在于java.nio , channels 包中的類,用于寫入、修改、讀取文件。此類的對象創(chuàng)建一個可搜索的文件通道,通過該通道執(zhí)行所有這些活動。這個類基本上提供了兩個方法,命名如下:
transferFrom(ReadableByteChannel src, long position, long count):將字節(jié)傳輸?shù)綇膕rc通道調(diào)用此方法的通道。這由目標(biāo)通道調(diào)用。該位置是指針的位置,從該位置開始復(fù)制操作。Count 指定文件的大小,它幾乎等于它包含的內(nèi)容量。
transferTo(long position, long count, WritableByteChannel target):將字節(jié)從源或方法調(diào)用通道傳輸?shù)轿募哪繕?biāo)通道。此方法主要使用源通道調(diào)用,Count 提到源文件的大小和要復(fù)制的位置
因此,我們可以使用這兩種方法中的任何一種來傳輸文件數(shù)據(jù)并復(fù)制它們。
例子:
// Java Program to Copy Files Using FileChannel Class
// Importing java.nio package for network linking
// Importing input output classes
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
// Main Class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
throws IOException
{
// Creating two channels one input and other output
// by creating two objects of FileChannel Class
FileChannel src
= new FileInputStream(
"C:\\Users\\Dipak\\Desktop\\input.txt")
.getChannel();
FileChannel dest
= new FileOutputStream(
"C:\\Users\\Dipak\\Desktop\\output.txt")
.getChannel();
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
// Transferring files in one go from source to
// destination using transferFrom() method
dest.transferFrom(src, 0, src.size());
// we can also use transferTo
// src.transferTo(0,src.size(),dest);
}
// finally keyword is good practice to save space in
// memory by closing files, connections, streams
finally {
// Closing the channels this makes the space
// free
// Closing the source channel
src.close();
// Closing the destination channel
dest.close();
}
}
}
輸出:
對于上述程序,我們需要一個 input.txt 和一個 output.txt 文件。最初,兩個文本文件看起來像這樣

程序執(zhí)行成功后,

這是java.nio.File包中的一個類。該類提供了 3 種復(fù)制文件的方法,如下所示:
copy(InputStream in, Path target):將輸入文件流中的所有字節(jié)數(shù)據(jù)復(fù)制到輸出文件的輸出路徑。它不能用于復(fù)制源文件中的指定部分。在這里,我們不需要創(chuàng)建輸出文件。它是在代碼執(zhí)行期間自動創(chuàng)建的。
copy(Path source, OutputStream out):將path source中指定的文件中的所有字節(jié)復(fù)制到輸出文件的輸出流中。
復(fù)制(路徑源,路徑目標(biāo)):使用源文件和目標(biāo)文件的路徑復(fù)制文件。也不需要在這里創(chuàng)建輸出文件。
例子:
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.io.*;
// save the file named as GFG.java
public class GFG{
// main method
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
// creating two channels
// one input and other output
File src = new File("C:\\Users\\Dipak\\Desktop\\input.txt");
File dest = new File("C:\\Users\\Dipak\\Desktop\\output.txt");
// using copy(InputStream,Path Target); method
Files.copy(src.toPath(), dest.toPath());
// here we are not required to have an
// output file at the specified target.
// same way we can use other method also.
}
}
輸出:
對于上述程序,我們需要一個 input.txt 和一個 output.txt 文件。最初,兩個文本文件看起來像這樣。
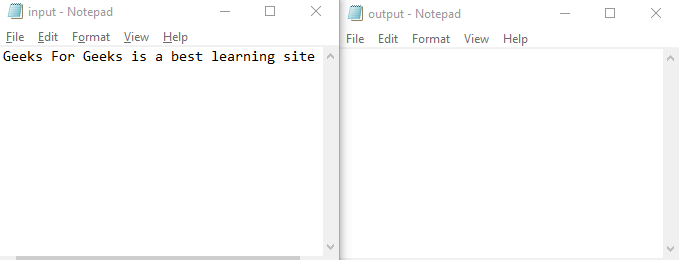
程序執(zhí)行成功后,
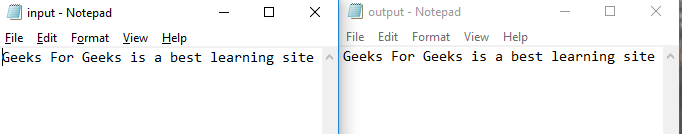
注意:在所有這些方法中,第一種方法的處理速度很快,但如果有人想要技術(shù)更先進(jìn),他們可以選擇其他兩種方法。FileChannel 方法還為我們提供了很多選項(xiàng)來控制要復(fù)制的文件部分并指定其大小。
以上就是關(guān)于“Java拷貝文件方法總結(jié)”,大家如果對此比較感興趣,想了解更相關(guān)知識,可以關(guān)注一下動力節(jié)點(diǎn)的Java在線學(xué)習(xí),里面的課程內(nèi)容從入門到精通,細(xì)致全面,很適合沒有基礎(chǔ)的小伙伴學(xué)習(xí),希望對大家能夠有所幫助。
相關(guān)閱讀



初級 202925

初級 203221

初級 202629

初級 203743