- Java基礎教程
- Java包(package)
- Eclipse安裝教程
- Java訪問權限
- Java Object類
- Java中final關鍵字的作用
- Java抽象類
- Java接口
- Java類與類之間的關系
- Java內部類
- Java數組的定義
- Java訪問數組元素
- Java數組元素的遍歷
- Java數組的靜態初始化
- Java數組引用數據類型
- Java可變長參數
- Java數組擴容
- Java數組的特點
- Java對象數組
- Java二維數組
- Java中arrays工具類
- Java數組算法
- Java中Collection集合概述
- Java中Collection的基本操作
- Java中List集合
- Java中ArrayList與Vector的區別
- Java中LinkedList詳解
- Java Set集合與HashSet集合特點
- Java TreeSet集合
- Java Collection集合小結
- Java中Collections工具類
- Java泛型詳解
- Java中Map集合概述
- Java中Map基本操作
- Java HashMap底層實現原理
- HashTable和HashMap的區別
- Java Properties類
- Java TreeMap排序
- Java Map集合小結
- Java IO流的分類
- Java文件輸入輸出流
- Java緩沖輸入輸出流
- Java數據輸入輸出流
- Java打印流與Java裝飾者設計模式
- Java對象輸入輸出流
- Java文件字符輸入輸出流
- Java字符輸入輸出流
- Java緩沖字符輸入輸出流
- Java File類概述
- File類常用操作
- Java線程概述
- Java創建線程的方式
- Java線程基礎操作
- Java線程的生命周期
- Java線程調度
- Java線程同步
- Java線程安全的類
- Java設計模式之生產者消費者模式
- Java Timer定時器
- Java線程死鎖
- Java反射概述
- Java反射類的信息
- Java反射字段信息
- Java反射方法
- Java反射構造方法
- Java反射創建實例
- Java通過反射訪問字段值
- Java通過反射調用方法
- Java Properties實例
Java字符串類型
String/StringBuffer/StringBuilder三個類,都是表示字符串的類
String類
● String對象的創建
package com.wkcto.chapter04.string;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* String對象的創建
* String類的構造方法
* @author 蛙課網
*
*/
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
//1) 直接賦值字符串字面量
String s1 = "wkcto";
//2) 無參構造
String s2 = new String(); //new運算符在堆區中創建一個String對象, 把該對象的引用保存到s2中
if ( s2 == null ) {
System.out.println("s2的值是null");
}else {
System.out.println("s2是一個長度為0的字符串,是一個空字符串"); //相當于""
}
//Person p1 = new Person(); new運算符在堆區中創建一個對象,把對象的引用保存到p1中
//3) 根據字節數組創建String對象
byte[] bytes = {65 , 66, 67, 97, 98, 99};
//把bytes字節數組中所有字節,根據當前默認的編碼(UTF-8)轉換為字符串對象
String s3 = new String(bytes);
System.out.println( s3 ); //ABCabc
//把字節數組中的部分字節轉換為字符串對象
s3 = new String(bytes, 0, 3); //把bytes字節數組從0開始的3個字節轉換為String對象
//字符串的getBytes()方法可以把字符串以當前默認的編碼轉換為字節數組
bytes = "wkcto是一個神奇的網站".getBytes(); //在UTF-8編碼中,一個英文占1字節,一個漢字占3個字節
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(bytes ));
//[119, 107, 99, 116, 111, -26, -104, -81, -28, -72, -128, -28, -72, -86, -25, -91, -98, -27, -91, -121, -25, -102, -124, -25, -67, -111, -25, -85, -103]
s3 = new String(bytes, 0, 8);
System.out.println( s3 );
s3 = new String(bytes, 4, 8);
System.out.println( s3 );
//把字符串轉換為指定編碼格式下對應的字節數組
bytes = "wkcto是一個神奇的網站".getBytes("GBK"); //在GBK編碼中, 一個英文占1字節,一個漢字占2字節
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(bytes ));
//[119, 107, 99, 116, 111, -54, -57, -46, -69, -72, -10, -55, -15, -58, -26, -75, -60, -51, -8, -43, -66]
s3 = new String(bytes); //把bytes字節數組按照當前默認編碼utf-8轉換為字符串
System.out.println( s3 );
s3 = new String(bytes, "GBK"); //把bytes字節數組中 字節按指定的編碼GBK轉換為字符串
System.out.println( s3 );
//4) 把字符數組轉換為字符串
char [] contents = {'w','k','很','牛','B'};
String s4 = new String(contents);
System.out.println( s4 );
s4 = new String(contents, 0, 2);
System.out.println( s4 );
//5)根據已有的字符串生成新的字符串對象
String s5 = new String(s3);
System.out.println( s5 );
System.out.println( s3 == s5 ); //false
System.out.println( s3.equals(s5)); //true
}
}
● String常用操作
char:charAt(int index) 返回指定索引位置的字符
int:compareTo(String anotherString) String類實現了Comaprable接口,可以比較兩個字符串的大小, 遇到第一個不相同的字符, 碼值相減
String:concat(String str) 在當前字符串的后面連接str字符串
boolean:contains(CharSequence s) 在當前字符串中判斷是否包含指定的字符串s, 如果包含返回true
boolean:endsWith(String suffix) 判斷當前字符串是否以suffix結尾
boolean:equals(Object anObject) 判斷兩個字符串的內容是否一樣
boolean:equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString)忽略大小寫
staticString:format(String format, Object... args) 字符串的格式化
byte[]:getBytes() 返回當前字符串在默認的編碼格式下對應的字節數組
byte[]:getBytes(String charsetName) 返回當前字符串在指定的編碼格式下對應的字節數組
void:getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char[] dst, int dstBegin) 把當前字符串[srcBegin,srcEnd) 范圍內的字符復制到dst數組中desBegin開始的位置
int:hashCode()
int:indexOf(int ch) 返回字符ch在當前字符串中第一次出現的位置
int:indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex). 返回字符ch在當前字符串中從fromIndex開始第一次出現的位置
int:indexOf(String str) 返回字符串str在當前字符串中第一次出現的位置
int:indexOf(String str, int fromIndex) 返回字符串str在當前字符串中從fromIndex開始第一次出現的位置
String:intern()返回當前字符串對應的字符串常量
boolean:isEmpty() 判斷當前字符串是否為空串
int:lastIndexOf(int ch) 返回字符ch在當前字符串中最后一次出現的位置
int:lastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex)
int:lastIndexOf(String str) 返回字符串str在當前字符串中最后一次出現的位置
int:lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex)
int:length() 返回字符串中字符的個數
boolean:matches(String regex) 判斷當前字符串是否匹配指定的正則表達式
String:replaceAll(String regex, String replacement) 把當前字符串中符合regex正則表達式的字符串替換為replacement
String[]:split(String regex) 使用正則表達式regex把當前字符串進行分隔
boolean:startsWith(String prefix)
String:substring(int beginIndex) 返回從beginIndex開始到最后的子串
String:substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) 返回從beginIndex開始到endIndex范圍內的子串
char[]:toCharArray() 把字符串轉換為字符數組
String:toLowerCase() 把大寫字母轉換為小寫字母
String:toString()
String:toUpperCase() 把小寫字母轉換為大寫字母
String:trim() 去掉前后的空白字符
staticString:valueOf(int i) 把基本類型轉換為字符串
staticString:valueOf(Object obj)
package com.wkcto.chapter04.string;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 演示String類的基本操作
* @author 蛙課網
*
*/
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
String str = "wkctoisthebest";
//1)charAt(index), length()
for(int i = 0 ; i<str.length() ; i++){
System.out.print( str.charAt(i) );
}
System.out.println( );
//2) contains()
System.out.println( str.contains("wkcto"));
System.out.println( str.contains("powernode"));
//3)字符串的比較
String str2 = "wkctogood";
System.out.println( str.compareTo(str2)); //2 'i' - 'g'
System.out.println("張三".compareTo("李四")); //-2094 '張'的碼值比'李'的碼值小
//4)equals()字符串內容的比較
System.out.println( str.equals(str2)); //fasle
//5)format()字符串的格式化,%s格式符對應字符串, %d格式符代表整數, %f格式符代表小數
System.out.println( String.format("姓名:%s,年齡:%d,工資:%f", "feifei", 28 , 30000.0));
// 姓名:feifei,年齡:28,工資:30000.000000
//6)getBytes()返回字符串對應的字節數組
byte[] bytes = "wkcto是一個神奇的網站".getBytes(); //在當前utf-8編碼下對應的字節數組
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(bytes));
bytes = "wkcto是一個神奇的網站".getBytes("GBK"); //在指定的GBK編碼下對應的字節數組
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(bytes));
//7) 把文件路徑 分離, 文件夾,文件名,擴展名
String path = "d:/Chapter04/src/com/wkcto/chapter04/string/Test02.java";
int lastSlashIndex = path.lastIndexOf("/");
int dotindex = path.indexOf(".");
String folder = path.substring(0, lastSlashIndex);
String filename = path.substring(lastSlashIndex+1 , dotindex);
String suffix = path.substring(dotindex+1);
System.out.println( folder );
System.out.println( filename );
System.out.println( suffix );
//8) trim()去掉前后的空白字符
str = " wkcto good ";
System.out.println( "aaaaa" + str.trim() + "BBBB");
//9) valueOf() 可以把其他類型轉換為字符串
str = String.valueOf( 456 );
str = "" + 789; //字符串與基本類型連接時, 先把基本類型轉換為字符串再連接
}
}
package com.wkcto.chapter04.string;
/**
* String中和正則表達式相關的方法
* 正則表達式就是一個模式串,常用于判斷字符串是否匹配指定的格式, 如判斷用戶名必須包含字母與數字,如判斷郵箱是否合理
* 正則表達式中的字符
* 轉義字符
* [abc] 匹配a/b/c中的一個
* [a-zA-Z] 小寫字母a~z或者大寫字母A~Z中的一個
* . 任意字符
* \d 數字
* \s 空白符, 空格, Tab, 回車
* \w 單詞字符 [a-zA-Z0-9_]
* X? 匹配0次或1次
* X* 任意次
* X+ 至少1次
* X{n} 正好n次
* X{n,} 至少n次
* X{n,m} 至少n次,最多m次
*
*
* @author 蛙課網
*
*/
public class Test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//判斷字符串是否匹配郵箱格式
String email = "[email protected]";
String regex = "[a-zA-Z1-9]\\w{4,30}@\\w{2,}\\.(com|cn)";
System.out.println( email.matches( regex ));
// 替換所有
String text = "wkcto123good";
text = text.replaceAll("\\d", "*"); //把替換后的字符串給返回
System.out.println( text );
//字符串的分隔
text = "wkcto is the best website.";
String [] words = text.split("[.,\\s]+");
for (String string : words) {
System.out.println( string );
}
}
}
● String字符串是不可變的
package com.wkcto.chapter04.string;
/**
* String對象是不可變的
* @author 蛙課網
*
*/
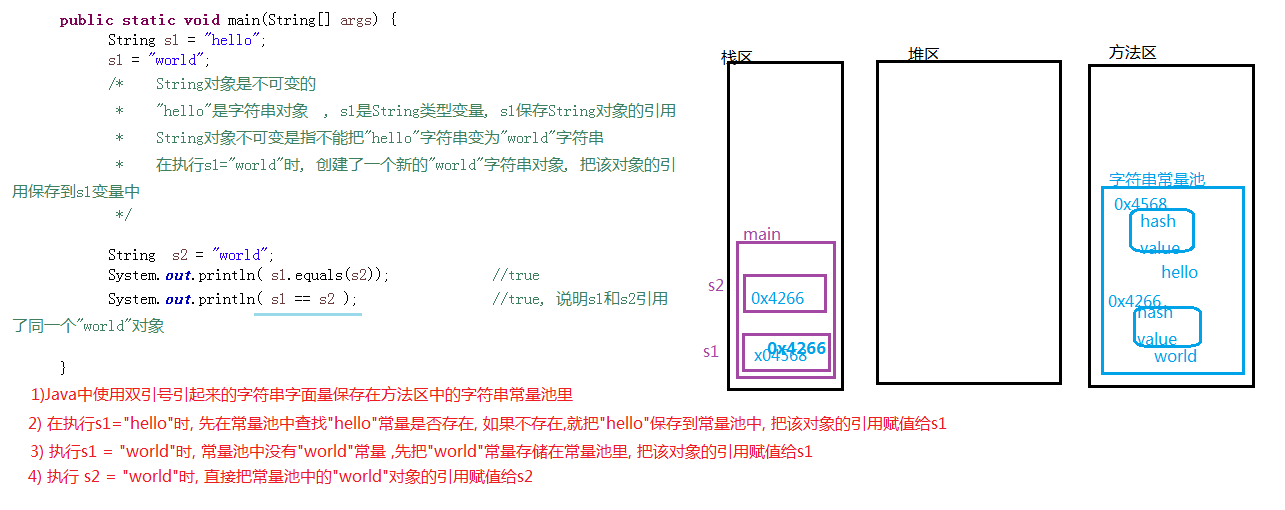
public class Test04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "hello";
s1 = "world";
/* String對象是不可變的
* "hello"是字符串對象 , s1是String類型變量, s1保存String對象的引用
* String對象不可變是指不能把"hello"字符串變為"world"字符串
* 在執行s1="world"時, 創建了一個新的"world"字符串對象, 把該對象的引用保存到s1變量中
*/
String s2 = "world";
System.out.println( s1.equals(s2)); //true
System.out.println( s1 == s2 ); //true, 說明s1和s2引用 了同一個"world"對象
//new運算符會在堆區中創建一個新的對象
String s3 = new String("hello");
String s4 = new String("hello");
System.out.println( s3 == s4 );
}
}
package com.wkcto.chapter04.string;
/**
* String對象是不可變的
* 每次進行字符串連接都 會生成新的字符串對象
* @author 蛙課網
*
*/
public class Test05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "wkcto";
String s2 = s1 + "bjpowernode";
/*
* 使用+運算符進行字符串連接時, 借助StringBuilder類實現
* 先根據s1創建一個StringBuidler對象, 假設叫sb
* 調用sb對象的append()方法把"bjpowernode"連接起來
* 最后調用sb對象的toString()方法,在該方法中創建一個新的String對象,并把該對象返回賦值給s2
*/
//以下兩行共創建了多少個String對象? 3個: 常量 :"abc", "def" 生成的新的對象"abcdef"
String s3 = "abc";
String s4 = s3 + "def"+ "abc" + "def";
//以下兩行共創建了多少個String對象? 3個: 常量 : "hehe", "he" , 生成新的: "hehehehe"
s3 = "hehe";
s4 = s3 + "he" + "he";
//以下兩行共創建了多少個String對象? 2個: 常量 : "haha", "hahahaha"
s3 = "haha";
s4 = "ha" + "ha" + s3; //javac編譯器,會把"ha"+"ha"常量的連接進行優化為"haha"
//以下兩行共創建了多少個String對象? 2個: 常量 : "heihei", new出來一個對象
s3 = "heihei";
s4 = new String("hei" + "hei"); //javac編譯器會把"hei"+"hei"優化為"heihei"
}
}
StringBuilder/StringBuffer
String對象是不可變的, 每次進行字符串的連接都會生成新的字符串對象, 如果需要頻繁進行字符串連接時, 不建議使用String字符串, 而是使用StringBuilder/StringBuffer
StringBuilder/StringBuffer稱為可變的字符串
package com.wkcto.chapter04.string;
/**
* StringBuilder/StringBuffer
* 1) 稱為可變的字符串
* 2) 最常用的方法是append(), 在當前字符串的后面追加另外一個字符串
* 3) 默認初始化大小: 16
* 4) 當value數組已滿,需要擴容, 按 value.length * 2 + 2 大小擴容
* 5) StringBuffer提供的方法都使用了synchronized進行了修飾, 是線程安全的.
* StringBuilder不是線程安全的
* @author 蛙課網
*
*/
public class Test06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String text = "";
for( int i = 1; i <= 100; i++){
text = text + i; //每次會生成新的字符串對象, 還會產生一些垃圾對象
}
//頻繁字符串連接, 使用StringBuilder/StringBuffer
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for( int i = 1; i <= 100; i++){
sb.append(i);
}
StringBuffer sb2 = new StringBuffer();
sb2.append("hello");
}
}






