- Java教程
- Java語言概述
- Java語言發展史
- Java語言的特性
- Java中JDK、JRE、JVM三者之間的關系
- Java程序的開發過程與運行過程
- 編寫第一個Java程序
- Java中的注釋
- Java中public class與class的區別
- Java控制語句概述
- Java選擇語句if
- Java switch選擇語句
- Java for循環語句
- Java while循環語句
- Java do while循環語句
- Java break語句
- Java continue語句
- Java return語句
- Java中this關鍵字是什么
- Java this關鍵字的使用(在實例方法中)
- Java this關鍵字的使用(在構造方法中)
- Java中static關鍵字
- Java中static靜態變量
- Java static靜態代碼塊
- Java static靜態方法
Java基礎編程練習題
十、 Java封裝練習題
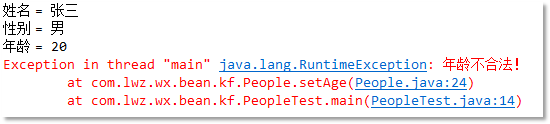
● 定義“人”類,“人”類包括這些屬性:姓名、性別、年齡等。使用封裝的方式編寫程序,要求對年齡進行安全控制,合法的年齡范圍為[0~100],其他值表示不合法。
public class People {
private String name;
private boolean sex;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String _name) {
name = _name;
}
public boolean isSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(boolean _sex) {
sex = _sex;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int _age) {
if(_age < 0 || _age > 100){
throw new RuntimeException("年齡不合法!");
}
age = _age;
}
}
public class PeopleTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
People p = new People();
p.setName("張三");
p.setAge(20);
p.setSex(true);
System.out.println("姓名 = " + p.getName());
System.out.println("性別 = " + (p.isSex() ? "男" : "女"));
System.out.println("年齡 = " + p.getAge());
p.setAge(-100);
}
}
十一、 this和static關鍵字練習題
● 選擇題(B)
public class Test {
static int value = 9;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
new Test().printValue();
}
public void printValue(){
int value = 69;
System.out.println(this.value);
}
}
B. 打印9
C. 打印69
D. 運行時拋出異常
● 判斷下面代碼的輸出結果,并說明原因
public class User {
private String name;
public User(){
}
public void setName(String name){
name = name;
}
public String getName(){
return name;
}
}
public class UserTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
User user = new User();
user.setName("zhangsan");
System.out.println(user.getName());
}
}
原因:setName方法體當中的name = name是把局部變量name賦值給局部變量name,和實例變量name無關,所以getName()方法獲取的實例變量值是null。
● 找出下面代碼的錯誤,并說明為什么錯了
public class Test {
int i;
static int j;
public void m1(){
System.out.println(i);
System.out.println(j);
m2();
m3();
}
public void m2(){
}
public static void m3(){
System.out.println(i);
System.out.println(j);
m2();
m4();
}
public static void m4(){
}
}
十二、Java繼承練習題
● 定義猴子類,猴子有名字和性別等屬性,并且定義猴子說話的方法,定義人類,人有名字和性別等屬性,并且定義人說話的方法。使用繼承,讓代碼具有復用性。
public class Monkey {
private String name;
private boolean sex;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public boolean isSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(boolean sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public Monkey() {
super();
}
public Monkey(String name, boolean sex) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
}
public void speak(){
System.out.println(name + "咿咿呀呀!");
}
}
public class People extends Monkey{
public void speak(){
System.out.println(this.getName() + ",呦,小伙會說話了!");
}
}
public class Animal {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Animal() {
super();
}
public Animal(String name) {
super();
this.name = name;
}
public void move(){
System.out.println(name + " is moving!");
}
}
public class Fish extends Animal{
public void move(){
System.out.println(this.getName() + "正在水里歡快的游來游去!");
}
}
● 實現憤怒的小鳥
我們有很多種小鳥,每種小鳥都有飛的行為,還有一個彈弓,彈弓有一個彈射的行為,彈射時把小鳥彈出去,之后小鳥使用自己飛行的行為飛向小豬(不要求編寫小豬的代碼)。不同種類的小鳥有不同飛行的方式:
紅火:紅色小鳥,飛行方式:正常
藍冰:藍色小鳥,飛行方式:分成3個
黃風:黃色小鳥,飛行方式:加速。
//小鳥
public class Bird {
//飛
public void fly(){
}
}
public class RedBird extends Bird{
public void fly(){
System.out.println("正常的飛翔");
}
}
public class BlueBird extends Bird{
public void fly(){
System.out.println("變成了3只小鳥一起飛");
}
}
public class YellowBird extends Bird{
public void fly(){
System.out.println("加速飛翔");
}
}
//彈弓
public class Slingshot {
//射
public void shot(Bird bird){
//鳥兒飛
bird.fly();
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Bird redBird = new RedBird();
Bird blueBird = new BlueBird();
Bird yellowBird = new YellowBird();
Slingshot ss = new Slingshot();
ss.shot(redBird);
ss.shot(blueBird);
ss.shot(yellowBird);
}
}
執行結果如下圖所示:
● 計算不同類型的員工薪資
定義員工類Employee,員工包含姓名name、出生月份birthMonth兩個屬性,員工有獲取指定月份工資的方法(getSalary(int month)),如果該月員工生日,公司補助250元。
定義有固定工資的員工類SalariedEmployee,有月薪monthlySalary屬性。
定義小時工類HourlyEmployee,包含工作小時數hours和每小時的工資hourlySalary屬性,如果每月工作超過160小時,超過的部分按1.5倍工資發放。
定義銷售人員類SalesEmployee,包含月銷售額sales和提成比例comm屬性。
public class Employee {
private String name;
private int birthMonth;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getBirthMonth() {
return birthMonth;
}
public void setBirthMonth(int birthMonth) {
this.birthMonth = birthMonth;
}
public double getSalary(int month){
return 0.0;
}
}
public class SalariedEmployee extends Employee {
private double monthlySalary;
public double getMonthlySalary() {
return monthlySalary;
}
public void setMonthlySalary(double monthlySalary) {
this.monthlySalary = monthlySalary;
}
public double getSalary(int month){
if(month == this.getBirthMonth()){
return monthlySalary + 250;
}
return monthlySalary;
}
}
public class HourlyEmployee extends Employee {
private int hours;
private double hourlySalary;
public int getHours() {
return hours;
}
public void setHours(int hours) {
this.hours = hours;
}
public double getHourlySalary() {
return hourlySalary;
}
public void setHourlySalary(double hourlySalary) {
this.hourlySalary = hourlySalary;
}
public double getSalary(int month){
double money = 0.0;
if(hours <= 160){
money = hourlySalary * hours;
}else{
money = hourlySalary * 160 + hourlySalary * (hours - 160) * 1.5;
}
if(month == this.getBirthMonth()){
money += 250;
}
return money;
}
}
public class SalesEmployee extends Employee {
private double sales;
private double comm;
public double getSales() {
return sales;
}
public void setSales(double sales) {
this.sales = sales;
}
public double getComm() {
return comm;
}
public void setComm(double comm) {
this.comm = comm;
}
public double getSalary(int month){
if(month == this.getBirthMonth()){
return sales * comm + 250;
}
return sales * comm;
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SalariedEmployee e1 = new SalariedEmployee();
e1.setName("張三");
e1.setBirthMonth(2);
e1.setMonthlySalary(5000.0);
System.out.println(e1.getName() + "的2月份工資是" + e1.getSalary(2));
HourlyEmployee e2 = new HourlyEmployee();
e2.setName("李四");
e2.setBirthMonth(2);
e2.setHourlySalary(50);
e2.setHours(170);
System.out.println(e2.getName() + "的2月份工資是" + e2.getSalary(2));
SalesEmployee e3 = new SalesEmployee();
e3.setName("王五");
e3.setBirthMonth(2);
e3.setSales(10000.0);
e3.setComm(0.5);
System.out.println(e3.getName() + "的2月份工資是" + e3.getSalary(2));
}
}
執行結果如下圖所示: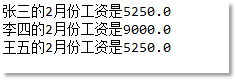
● 某汽車租賃公司有多種汽車可以出租,計算汽車租金
Vehicle是所有車的父類,屬性:品牌、車牌號,有返回總租金的方法:public double getSumRent(int days){}
小轎車類Car是Vehicle的子類,屬性:車型(兩廂、三廂、越野),兩廂每天300,三廂每天350,越野每天500。
多座汽車類Bus是Vehicle的子類,屬性:座位數,座位數<=16的每天400,座位數>16的每天600。
編寫測試類,根據用戶選擇不同的汽車,計算總租金。
public class Vehicle {
private String brand;
private String licensePlateNumber;
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public String getLicensePlateNumber() {
return licensePlateNumber;
}
public void setLicensePlateNumber(String licensePlateNumber) {
this.licensePlateNumber = licensePlateNumber;
}
public Vehicle() {
super();
}
public double getSumRent(int days){
return 0.0;
}
}
public class Car extends Vehicle {
//車型:兩廂(300/天)、三廂(350/天)、越野(500/天)
private String models;
public String getModels() {
return models;
}
public void setModels(String models) {
this.models = models;
}
public Car() {
super();
}
public double getSumRent(int days){
if("兩廂".equals(models)){
return 300 * days;
}else if("三廂".equals(models)){
return 350 * days;
}else{
return 500 * days;
}
}
}
public class Bus extends Vehicle {
//座位數
private int seats;
public int getSeats() {
return seats;
}
public void setSeats(int seats) {
this.seats = seats;
}
public Bus() {
super();
}
public double getSumRent(int days){
if(seats <= 16){
return 400 * days;
}else{
return 600 * days;
}
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car c = new Car();
c.setBrand("寶馬");
c.setLicensePlateNumber("京A 88888");
c.setModels("三廂");
System.out.println("品牌:" + c.getBrand() + ",車牌號:" + c.getLicensePlateNumber() + ",10天總租金:" + c.getSumRent(10));
Bus b = new Bus();
b.setBrand("海格");
b.setLicensePlateNumber("京B 88888");
b.setSeats(60);
System.out.println("品牌:" + b.getBrand() + ",車牌號:" + b.getLicensePlateNumber() + ",10天總租金:" + b.getSumRent(10));
}
}
執行結果如下圖所示:
十四、 super關鍵字練習題
● 請判斷以下代碼的輸出結果
public class Text {
public static int k = 0;
public static Text t1 = new Text("t1");
public static Text t2 = new Text("t2");
public static int i = print("i");
public static int n = 99;
public int j = print("j");
static {
print("靜態塊");
}
public Text(String str) {
System.out.println((++k) + ":" + str + " i=" + i + " n=" + n);
++i;
++n;
}
public static int print(String str) {
System.out.println((++k) + ":" + str + " i=" + i + " n=" + n);
++n;
return ++i;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
new Text("init");
}
}